Unlocking Business Potential with SAP as an ERP System
In the competitive landscape of modern business, efficiency and streamlined operations are critical for success. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have emerged as essential tools for integrating and managing business processes. Among these systems, SAP stands out as a leading solution, renowned for its comprehensive features and robust performance. This article delves into the advantages, functionalities, and implementation strategies of SAP as an ERP system, highlighting its impact on businesses of all sizes and sectors.
What is SAP ERP?
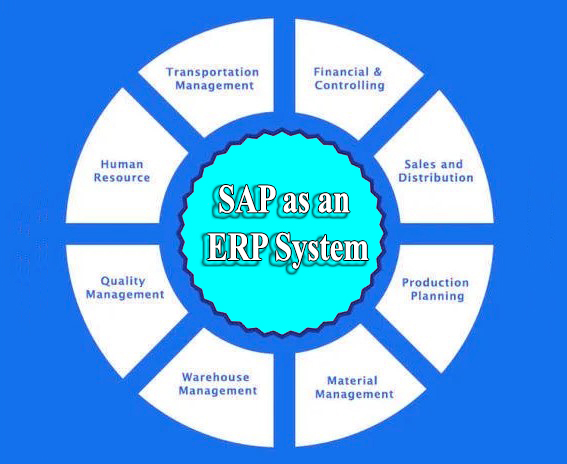
SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a software solution developed by SAP SE, a German multinational company founded in 1972. SAP ERP integrates various business processes and functions into a single unified system, enabling organizations to manage their operations more effectively. The system covers a wide range of business functions, including finance, human resources, procurement, supply chain management, and customer relationship management.
Key Features of SAP ERP
- Comprehensive Integration: SAP ERP seamlessly integrates different business processes and departments into one cohesive system. This integration ensures that data flows smoothly across the organization, reducing data silos and improving communication.
- Real-Time Data Processing: The ability to process data in real-time is one of SAP ERP’s most significant advantages. This feature allows businesses to make informed decisions quickly, respond to market changes promptly, and improve overall operational efficiency.
- Scalability: SAP ERP is designed to grow with your business. Whether you are a small enterprise or a large corporation, SAP can scale to meet your needs, handling increased data volumes and more users without sacrificing performance.
- Customization: The system is highly customizable, allowing businesses to tailor it to their specific needs. From custom workflows to personalized dashboards, SAP ERP can be adapted to fit unique business processes and industry requirements.
- Advanced Analytics and Reporting: SAP ERP includes powerful analytics and reporting tools that provide deep insights into business performance. These tools help organizations track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
- Robust Security: Security is a critical component of SAP ERP. The system includes advanced security features such as user authentication, role-based access control, and data encryption to protect sensitive business information.
Benefits of Implementing SAP ERP
- Increased Efficiency: By automating routine tasks and integrating various business functions, SAP ERP significantly improves operational efficiency. Employees can focus on strategic activities, leading to higher productivity and reduced operational costs.
- Enhanced Collaboration: With a unified system, departments can collaborate more effectively. SAP ERP provides a single source of truth, ensuring that all employees have access to the same data, which enhances communication and teamwork.
- Better Decision-Making: Real-time data processing and advanced analytics provide valuable insights that support informed decision-making. Businesses can quickly respond to market changes, optimize processes, and identify new opportunities.
- Regulatory Compliance: SAP ERP helps businesses stay compliant with industry regulations and standards. The system includes built-in compliance checks and risk management features that ensure adherence to legal requirements and reduce the risk of non-compliance.
- Cost Savings: While the initial investment in SAP ERP can be substantial, the long-term cost savings are significant. Improved efficiency, reduced errors, and optimized resource allocation contribute to lower operational costs.
Implementation Considerations
- Clear Objectives and Requirements: Define clear objectives and requirements before starting the implementation. Understanding what you aim to achieve with SAP ERP and how the system will support your business goals is crucial.
- Choose the Right Implementation Partner: Selecting the right implementation partner is critical for success. Look for a partner with extensive experience in SAP ERP implementations and a deep understanding of your industry. A good partner will guide you through the process, provide valuable insights, and ensure a smooth implementation.
- Effective Project Management: Effective project management is vital for a successful SAP ERP implementation. Assign a dedicated project manager to oversee the implementation, manage timelines, and coordinate with various stakeholders.
- Data Migration: Data migration is a critical step in the implementation process. Ensure that your data is clean, accurate, and well-organized before migrating it to the new system. Data quality issues can lead to significant problems down the line.
- Employee Training and Change Management: Comprehensive employee training and effective change management are essential components of a successful implementation. Provide thorough training to ensure that employees are comfortable using the new system. Additionally, manage the change process to address any resistance and ensure a smooth transition.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Thorough testing is necessary to identify and address any issues before going live. Conduct various tests, including unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing, to ensure that the system functions as expected.
- Post-Implementation Support: Post-implementation support is crucial to address any issues that arise after the system goes live. Ensure that you have a support plan in place to provide ongoing assistance and maintenance.
Real-World Applications of SAP ERP
- Manufacturing: SAP ERP is widely used in the manufacturing industry to streamline production processes, manage supply chains, and optimize inventory levels. Real-time data processing helps manufacturers respond to demand fluctuations and improve overall efficiency.
- Retail: In the retail industry, SAP ERP supports inventory management, sales tracking, and customer relationship management. The system helps retailers enhance the customer experience, optimize stock levels, and improve sales performance.
- Healthcare: Healthcare organizations use SAP ERP to manage patient records, streamline administrative processes, and ensure compliance with regulations. The system improves patient care by providing healthcare professionals with quick access to accurate information.
- Finance: SAP ERP is a valuable tool for financial institutions, providing robust financial management capabilities, including accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting. The system helps financial institutions ensure compliance and improve financial performance.
- Public Sector: Government agencies use SAP ERP to manage public services, streamline administrative processes, and enhance transparency. The system supports budgeting, procurement, and human resource management, contributing to more efficient public service delivery.
Conclusion
SAP ERP is a powerful and versatile tool that can transform business operations, improve efficiency, and support growth. By integrating various business processes, providing real-time insights, and offering extensive customization options, SAP ERP helps businesses stay competitive in a rapidly changing market. However, successful implementation requires careful planning, effective project management, and ongoing support. By understanding the key features, benefits, and implementation considerations, businesses can harness the full potential of SAP ERP and achieve their strategic goals.
Whether you are a small business looking to streamline operations or a large enterprise seeking to enhance efficiency and competitiveness, SAP ERP offers a comprehensive solution to meet your needs. Embrace the power of SAP ERP and unlock your business’s potential for greater success and growth.